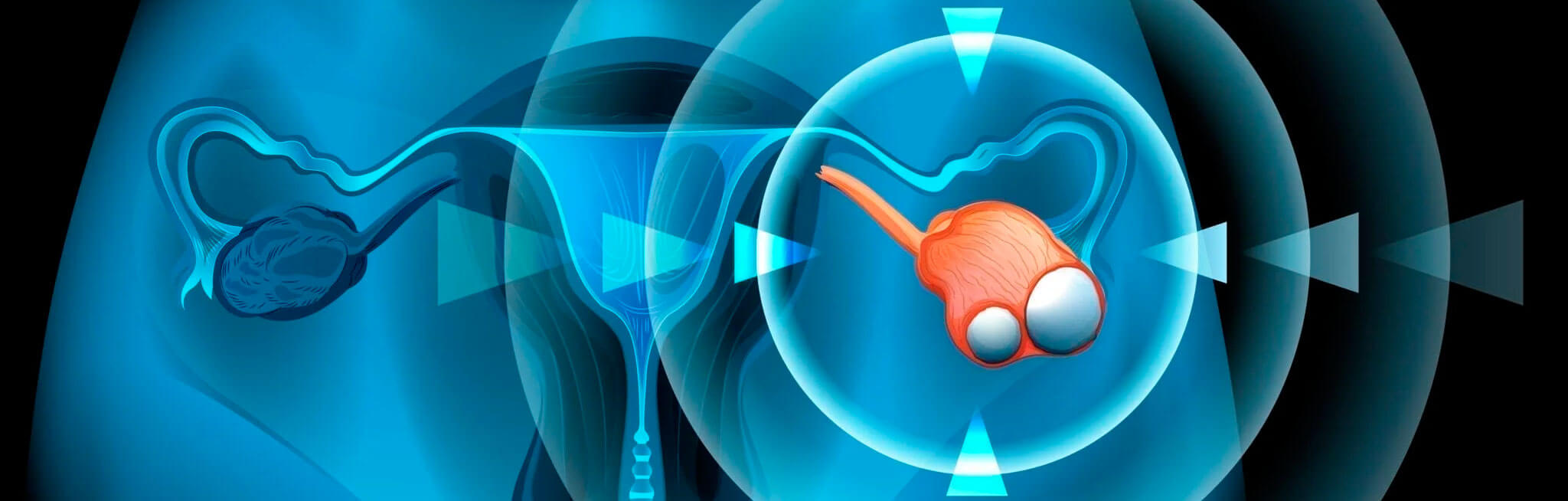
Ovarian Cysts
Request a quick appointment with the specialist in Ovarian Cysts, Dr. Lucas Minig, an expert Gynecologist Oncologist in this type of cancer that is very common in women.
Appointment: Click to Request an Appointment for ovarian cancer in Spain.
Contact: +34 679 112 179
What are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are formations that usually have liquid contents and rarely can have solid structures inside. Ovarian cysts are sacs of fluid in the ovary that measure more than 3 cm, of a benign nature, round or oval, with a thin wall. Ovarian cysts typically do not have solid parts inside and normally measures less than 10 cm.
On the other hand, we have the complex ovarian cysts filled with any combination of blood, solid matter, and liquid.
Every month in the ovaries appear cysts of 2-3 cm, even larger, which are follicles that grow until they rupture and produce ovulation. When the follicle breaks, bleeding sometimes occurs and we have a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst.
However, on some occasions they do not disappear after the period, continuing to grow after ovulating and usually disappear around 3-6 months.
They are very common in women up to 40-45 years of age and the vast majority usually remit spontaneously without giving symptoms. However, on rare occasions, they may be large enough to cause symptoms and require specific treatment.
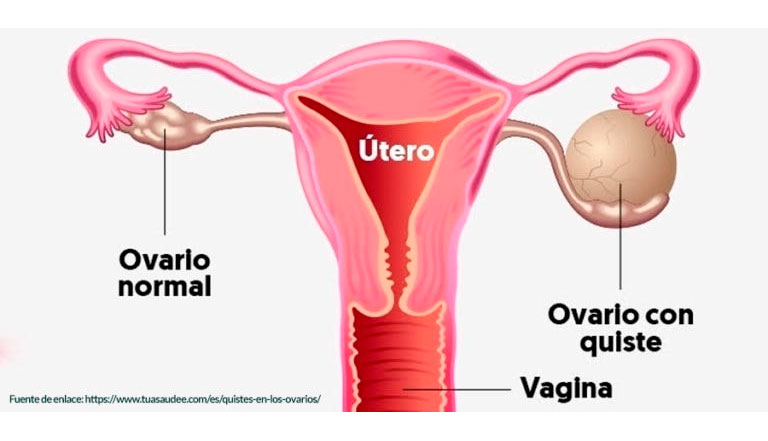
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Most cysts are diagnosed by chance, and it is very common not to have any symptoms to detect them.
The most frequent symptoms are:
- Nonspecific pelvic pain
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Abdominal distension
- Urgency to urinate or defecate
How Are Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of ovarian cysts is made by physical examination and gynecological ultrasound. The determination of the value of the tumor marker CA 125 and magnetic resonance imaging are usually only useful in selected cases to more accurately determine the content of the cyst, determine some additional characteristics, and establish the probability of malignancy or not of the ovarian cyst
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts can be physiological and organic.
- Physiological ovarian cysts: they always occur in women of childbearing age, before menopause, they are usually small (up to 4-5 cm) and usually disappear spontaneously after 2-3 periods.
- Organic ovarian cysts: do not disappear spontaneously. They tend to remain stable or grow over time. Certain types of cysts such as those of endometriosis disappear spontaneously with menopause.
- Benign: endometriosis, teratoma, cystadenomas
- Borderline tumors: serous, endometrioid, mucinous
- Malignant tumors: serous, endometrioid, mucinous, clear cell
The degree of suspicion arises from combining:
- The sonographic characteristics of the cyst
- The value of CA 125
- The age of the patient.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian Cysts usually disappear spontaneously after a few months. However, if they are large, cause symptoms, or have certain sonographic features, the cysts should be surgically removed.
There are three ways to monitor and treat Ovarian Cysts:
- Do nothing
- Follow-up after 1-2 months
- Surgery
Certain drugs such as oral contraceptives are beneficial to prevent new cysts from forming, but not to make the existing ones disappear.
Surgical Options For Managing Ovarian Cysts
Surgical Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
It is very important that surgery on the ovaries, both in young women and in those with suspected cancer, is performed by properly trained professionals. This, on the one hand, will reduce the trauma to the ovary to a minimum and, on the other hand, it will be able to give a more accurate treatment in the case of a malignant tumor.
Surgical procedures to treat an ovarian cyst include:
- Ovarian cystectomy: Removal of the ovarian cyst with its preservation.
- Adnexectomy: It consists of the removal of one or both ovaries and tubes (uterine adnexa).
There are 2 ways to perform a Cystectomy / Adnexectomy:
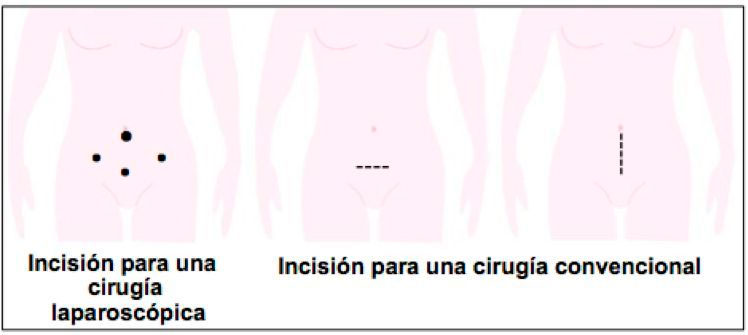
- Laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery: Today, practically 100% of ovarian cysts that require surgical treatment are operated on using laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery. The main exception is those large ovarian cysts that make it impossible to approach them through the millimeter holes of minimally invasive surgery.
- Traditional or open surgery: It is done through an abdominal incision. Depending on the size of the cyst and the previous suspicion regarding its benign or malignant origin, the incision may be horizontal or vertical.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cysts
What symptoms can ovarian cysts cause?
- Nonspecific pelvic pain
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Abdominal distension
- Urgency to urinate or defecate
How are ovarian cysts diagnosed?
The diagnosis of ovarian cysts is made by physical examination and gynecological ultrasound. Nuclear magnetic resonance is usually only useful in selected cases to more accurately determine its content and determine some additional characteristics.
Opinions of patients With Ovarian Cysts
Doctor Lucas Minig Specialist in Ovarian Cysts in Valencia, Spain
Contact the Ovarian Cyst Specialist
Leave us your data and consultation to offer you personalized medical advice
International Consultation
If you want remote medical care, you can consult
through the following links:
International Appointment
Online Consultation
Whatsapp: + 34 679 112 179