What Is Gynecological Cancer?
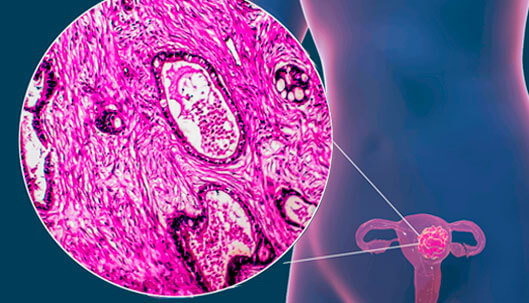
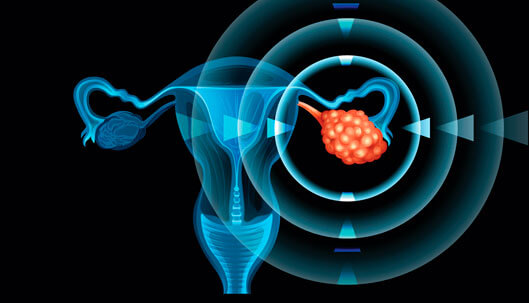
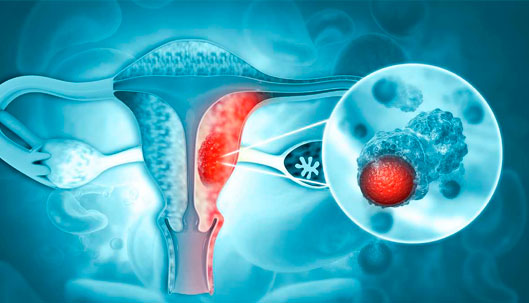
Gynecologic cancer is any cancer that starts in a woman’s reproductive organs. These types of cancer are identified depending on the part of the body where they first occur. Gynecological cancers originate in different reproductive organs located in the pelvic area, that is, the area below the stomach and between the hips.
It is possible to reduce the risk by avoiding estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy, maintaining a healthy weight, doing daily physical exercise, and a thorough check-up by your gynecologist in case of family history, risk factors, taking tamoxifen, or any genital bleeding.
Types of gynecological cancer
Of all gynecologic cancers, only cervical cancer has screening tests that can identify this cancer early, when treatment may be most effective.
Because there is no simple, reliable way to screen for gynecologic cancers other than cervical cancer, it’s especially important to recognize the warning signs and learn what you can do to reduce your risk.

What are the symptoms of gynecological cancer?
Frequent or urgent need to urinate and/or constipation are common in ovarian and vaginal cancers. Itching, burning, pain, or tenderness of the vulva and changes in the color or skin of the vulva, such as a rash, ulcers, or warts, are common only in vulvar cancer.
What causes
gynecological cancer?
What are the risk factors for gynecologic cancer? Cervical cancer. – HPV or human papilloma virus. – Being a smoker.
Patient Help
Prevention of gynecological cancer
Early diagnosis sometimes becomes the best prevention.
- Cáncer Ginecológico
- Cáncer Ginecológico
- PMID: 35302882
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.02016