Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Infection and Pre-Malignant Lesions of the Cervix
Request a quick Appointment with the specialist in the Human Papillomavirus disease known as HPV, Dr. Lucas Minig, an expert Gynecologist Oncologist in the city of Valencia, Spain.
Appointment: Click to Request an Appointment for ovarian cancer in Spain.
Contact: +34 679 112 179
Get to know the CV, Training and Biography of Lucas Minig.
What Is HPV and How Is HPV Infection Transmitted?
Pre-malignant diseases of the uterine cervix are caused by a sexually transmitted infection: the human papillomavirus (HPV).
If not properly diagnosed and treated, these pre-malignant conditions can progress to cervical cancer over many years.
Request assistance in Valencia Spain with Dr. Lucas Minig, a specialist in HPV disease known as Human Papillomavirus.
What are the main characteristics in reaction to the form of contagion of HPV infection?

How Is HPV Infection Diagnosed?
This test detects the presence of the virus in the blood that causes pre-malignant lesions of the cervix or cervical cancer.
The HPV virus is actually a family of numerous virus sub-types (nearly 200) that fall into two categories:
- Low risk: Two of the most common low-risk HPV subtypes are 6 and 11. They cause genital warts but do NOT cause cervical cancer.
There are two kinds:
- Warts located on the external genitalia (easily seen): these warts are caused by certain types of HPV, especially types 6 and 11. However, the types 6 and 11 viruses are unlikely to cause cancer. These types are transmitted through sexual contact and infect the genital and anal areas.
- Warts located on the internal genitalia (less visible): Other types of HPV, especially types 16 and 18, infect the genital area, but do not give rise to visible warts easily. They produce tiny flat warts on the cervix or anus that are only visible with a magnifying instrument called a colposcope. Warts can also appear in the vagina, vulva, and urethra.
- High risk: Two of the most frequent high-risk HPV subtypes are 16 and 18. They can stimulate the uncontrolled growth of cervical cells and cause pre-malignant lesions and, later, cancer.
How is the Diagnosis of Pre-Malignant Lesions and Cervical Cancer Made?
All women who have had sexual intercourse should periodically go to the gynecologist from the age of 25 to carry out tests with the aim of preventing female cancer.
Among them, the most important is to perform cervical cytology to detect pre-malignant lesions or cervical cancer in its very early stages.
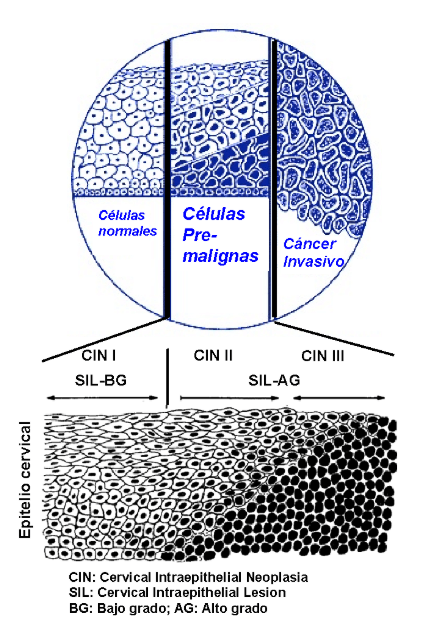
Pre-malignant lesions are controllable, either with simple follow-up (SIL BG) or with a small surgical treatment (SIL AG) to remove the lesion from the uterine cervix (cervical conization).
It is currently known that almost 100% of pre-malignant lesions and cervical cancer are caused by HPV infection.
KEY POINTS:
What Are the Different Types of Pre-Malignant Diseases?
Cytology can report the following results:
- Normal
- SIL of BG or low-grade intraepithelial lesion: represents the beginning of pre-cancer diseases of the cervix
- SIL of AG or high-grade intraepithelial lesion: means the evolution of the above and, without proper diagnosis and treatment, could progress to cervical cancer
- ASCUS-AGUS: means a cytology result of uncertain significance. It must be repeated because, generally, pathologists cannot make a diagnosis based on the remitted sample.
- Cancer
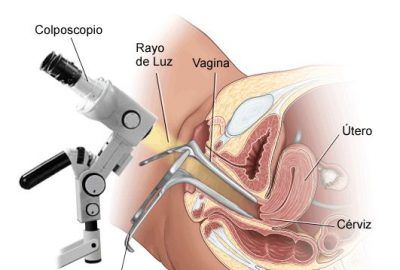
What is a Colposcopy And How Is It Used To Diagnose Malignant Disease in the Cervix?
The next step is to perform a colposcopy. This consists of a direct visual examination through a colposcope to assess the surface of the cervix and vagina.
The colposcope is a kind of microscope that works like a magnifying glass that increases the surface of the cervix from 6 to 40 times, allowing the evaluation of different lesions at the level of the cervix, and that are imperceptible to the human eye.
The exam bothers more than taking the cervical cytology.
What to Do If Colposcopy Shows Suspicious Lesions?
If the colposcopy reveals abnormal lesions in the cervix, a targeted biopsy should be performed.
The biopsy consists of taking a small portion of tissue to analyze through a pathological anatomy study and thus define what type of injury that organ presents and guide a possible treatment.
Cervical or vaginal biopsies are mildly painful and are usually performed in the same office. They are performed using special forceps under colposcopic guidance to offer greater precision at the site of the sample.
It is essential to perform them to confirm the diagnosis since the cervical biopsy is more precise. In this way, a suitable treatment plan can be defined for each patient and for each particular injury.
Treatment may include surgical procedures as an effective resolution for malignant cervical abnormalities.
Medical information developed by Gynecologist Oncologist Lucas Minig, specialist in Human Papilloma Virus in Valencia, Spain.
Frequently Asked Questions about Human Papillomavirus
Frequently Asked Questions about Human Papillomavirus
How is the diagnosis of HPV made?
HPV infection does not usually cause symptoms. They are usually diagnosed at the time of performing the annual cervical cytology. In certain cases, some women may present warts at the vulvar level that may alert the woman to consult a specialist.
What are the risk factors for acquiring HPV?
- The beginning of sexual relations at an early age
- Multiple sexual partners
- Age: the highest incidence of this cancer is observed around 40-50 years. However, at younger ages, pre-malignant lesions that can cause cervical cancer throughout life are more frequent.
- Smoking: tobacco is a strong immunosuppressant. Its effect is further enhanced if the woman has some type of HPV in her blood.
- Immunosuppression: HIV (the virus that causes AIDS), diabetes, transplants.
- Oral contraceptives for long periods of time (usually more than 5 years)
- Have 3 or more children
If women have one of these diseases or conditions, it does not mean that they will have HPV infection or cervical cancer in the future, only that it is necessary to discuss it with their gynecologist.
Should I tell my partner?
If you have an HPV infection, it is recommended that your sexual partner see a doctor for a check-up.
Help and information
If you suspect that you may have an HPV infection or another sexually transmitted infection, see your specialist doctor.
What should I do to improve myself?
Your diagnosis can be sped up by having a Pap smear done on the area. A cervical exam (visual inspection) can also detect warts and other abnormal growths, so seeing a gynecologist is helpful. Consultation with the Gynecologist Lucas Minig in Spain.
HPV epidemiology
How is HPV transmitted?
By sexual intercourse and vertical route (mother-child during childbirth). It is the most common sexually transmitted disease. 80% of women have been infected with some type of HPV.
What pathologies are related to HPV?
The benign pathologies with which it is related are warts in general.
What factors protect against HPV?
The use of condoms protects 70% from HPV infection.
How does the infection evolve?
90% of infections are effectively resolved by the patient within 2 years.
Contact the HPV Specialist in Spain
Leave us your data and consult to offer you personalized medical advice on HPV.
Contact the Human Papilloma Virus Specialist
Leave us your data and consultation to offer you personalized medical advice
International Consultation
If you want remote medical care, you can consult
through the following links:
International Appointment
Online Consultation
Whatsapp: + 34 679 112 179