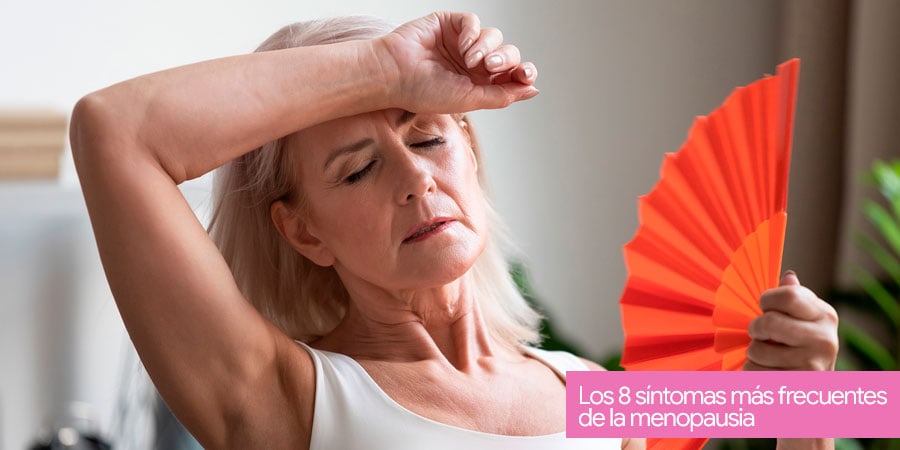

The 8 most common symptoms of menopause
Menopause is a natural state in a woman’s life, in which the hormonal function of the ovaries ceases and, therefore, is expressed with the definitive absence of menstruation. Generally, this happens between 45-55 years, the usual average being 50 years.
In this article, we explain how to recognize the symptoms of menopause in women.
How is menopause diagnosed?
The diagnosis of menopause is made when the woman spends at least 1 year without menstruation. Any alteration that is expressed around that period is called perimenopause or climacteric.
During this period, the transition between the reproductive and non-reproductive stages of women occurs. This is due to the gradual decrease in the production of estrogen and progesterone that generates, among other symptoms of menopause, the cessation of menstruation.
Surgical menopause, on the other hand, is produced artificially by surgical removal of the ovaries.
In the case of hysterectomy, or removal of the uterus, it also generates an absence of menstruation, but this does not represent menopause since the ovaries will continue their function until it ceases. Therefore, a hysterectomy does not condition early menopause.
What are the symptoms of menopause?
Some of the first symptoms of menopause that you can feel in your body are:
Menstrual disturbances
Menstrual disturbances represent the most common symptom of premenopause and appear early.
Menstrual cycles can become shorter or longer, with more or less menstrual flow. This is due to a progressive absence of ovulation. Generally, the cycles are spaced more and more with the consequent disappearance of menstruation.
Vaginal dryness
After menopause, the mucous membranes, and especially the vagina, suffer progressive thinning with the alteration of lubrication that causes dryness. Therefore, it is common for women to complain of vulvovaginal itching or discomfort with sexual intercourse.
This physical symptom of menopause is usually transitory and not all women present it.
The decrease in estrogen during menopause can also predispose to a higher risk of urinary tract infection.
Hot flashes
Hot flashes are an expression of the alteration in the vasomotor system due to menopause. They consist of a sensation of heat that they describe as ascending from the neck to the face and that can cause palpitations and sweating. They can last from 30 seconds to a few minutes.
Although they can happen at any time of the day, they usually appear at night. It is a symptom of menopause that can significantly alter the quality of life but is usually transitory, lasting approximately a few years after the onset of menopause.
Sleep disturbance
Sleep problems are a very common symptom of menopause in women. In turn, they may also wake up early with difficulty going back to sleep at night. This, added to hot flashes or hot flashes at night, usually significantly alters the quality of life in some women during menopause.
Mood disorders
Emotional alterations, although less frequent than the previous ones, make up one of the most difficult symptoms to treat. It can manifest with emotional ups and downs, irritation, or sadness. They are the most common, which can be included in a more important depression.
In some women, this symptom can begin premenopausal and, in certain cases, treatment must involve specific medication to control the mood and emotional state of women. Fortunately, it is a transient symptom of menopause.
Decreased libido
The sexual desire usually decreases as a result of the drop in estrogen levels in women during menopause. It is usually accompanied, in turn, by an alteration in the perception of one’s own body.
Although it can alter the sentimental balance of the partner itself, it is important that the sentimental partner knows this symptom during the menopause of women and can accompany her during this process.
Body changes and weight gain
Menopause is usually accompanied by some metabolic changes and physical symptoms, such as the onset of diabetes, hypertension, overweight, and obesity.
These physical changes of menopause are due to an increase in body fat where a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet can accelerate this process.
Women, after menopause, may have an increased risk of heart attacks. For this reason, it is recommended that they visit their GP or family doctor regularly for global health control during menopause.
Osteopenia and osteoporosis
Osteopenia and osteoporosis are other symptoms of menopause. It is the progressive bone demineralization that is generated by the decrease in estrogen levels in the blood due to the decline in ovarian function.
Although it is important to mention that all women will suffer a certain degree of bone demineralization during menopause, excessive loss of calcium can lead to osteoporosis, which symbolizes a significant fragility of the bones with a higher risk of fractures.
Other factors can contribute to the acceleration of this process, such as immobilization, the use of corticosteroids, anorexia nervosa, smoking, and early menopause, among others.
![[:es]Telemedicina Médico remoto en España NOTICIA[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/telemedicina-medico-remoto-doctor-espana-lucas-minig.jpg)
![[:es]La quimioterapia hipertérmica intraperitoneal (HIPEC), no es útil en mujeres con cáncer de ovario[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/quimioterapia-hipertermica-intraperitoneal-no-util-cancer-de-ovario.jpg)
![[:es]Vacuna Contra VPH reduce cáncer de útero[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/vacuna-contra-vph-noticias-dr-lucasminig.jpg)
![[:es]Investigan cómo prevenir el cáncer de ovario. Doctor Lucas Minig[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/prevenir-cancer-de-ovario-mujeres-con-alto-riesgo-drlucasminig-investigacion.jpg)
