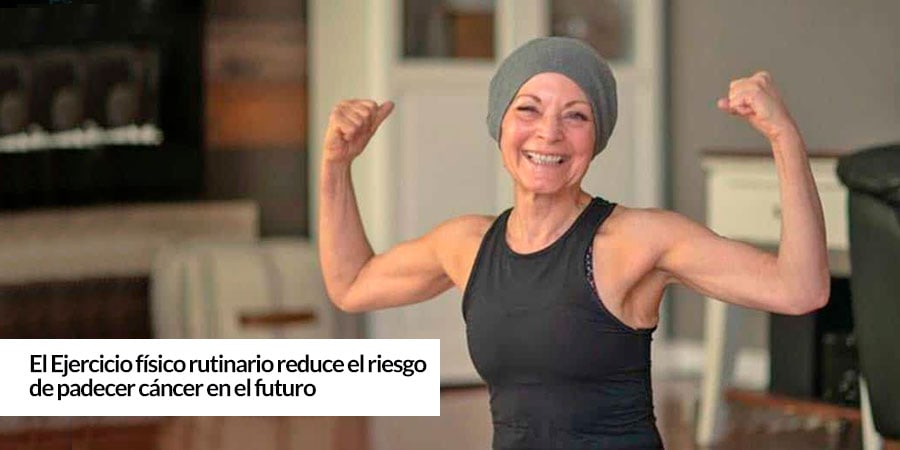

Regular physical exercise reduces the risk of cancer in the future
What is the physics activity?
Physical activity is any movement that is physical and requires more energy than resting. Physical activity can include walking, running, swimming, bicycling, dancing, housework, and exercising, among others.
The metabolic equivalent of exercise (MET) is a way to standardize the intensity of physical activity. One MET is the rate of energy expended by a person sitting at rest. To give you an idea, when a person is exercising with an intensity of 15 METs, it means that he is exercising at an intensity 15 times greater than what he would do at rest. Thus, the MET is divided into 3 categories according to its intensity:
● LIGHT: when physical activity consumes less than 3 METs;
● MODERATE: if between 3 and 6 METs are consumed; or
● INTENSE: in case of consuming 6 or more METs.
Sedentary behavior, by contrast, is any waking behavior characterized by an energy expenditure of 1.5 METs or less. Examples of sedentary behaviors include most office work, sitting on the couch, or driving a car, for example.
What is known about the relationship between physical activity and cancer risk?
A study recently published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology analyzed the results of 9 prospective epidemiological cohort studies. The study compared 755,459 cancer-free participants followed for a median time of 10.1 years with 50,620 cancer patients. Physical activity of 7.5 – 15 METs was associated with a significant reduction in future cancers: colon, breast, endometrial, kidney, myeloma, and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Why is the physical activity associated with reduced cancer risk?
Exercise has many biological effects on the body, some of which have been proposed to explain associations with specific cancers. These include:
● Decrease the levels of sex hormones, such as estrogen, and growth factors that have been associated with the development and progression of breast, or colon cancer, among others.
● Prevention of high levels of insulin in the blood, which has been linked to the development and progression of breast, or colon cancer, for example.
● Reduction of inflammation
● Improvement of the function of the immune system.
● Alteration of the metabolism of bile acids, decreasing the exposure of the gastrointestinal tract to substances that predispose to cancer, such as colon cancer.
● Helps prevent obesity, which is a risk factor for many types of cancer.
How much physical activity is recommended?
The main scientific societies make the following recommendations to obtain substantial health benefits and reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including cancer:
● Perform 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, 75 to 100 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of each intensity per week. This physical activity can be done in bouts of any duration.
● Do muscle-strengthening activities at least 2 days a week.
![[:es]Vacuna protección contra cáncer de cuello uterino[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/vacuna-1-dosis-contra-vph-proteccion-cancer-cuello-uterino.jpg)
![[:es]Extirpar Utero no es necesario Extirpar los ovarios[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/logotipo-lucas-minig.jpg)
![[:es]Telemedicina Médico remoto en España NOTICIA[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/telemedicina-medico-remoto-doctor-espana-lucas-minig.jpg)
![[:es]La quimioterapia hipertérmica intraperitoneal (HIPEC), no es útil en mujeres con cáncer de ovario[:]](https://drlucasminig.com/en/wp-content/uploads/quimioterapia-hipertermica-intraperitoneal-no-util-cancer-de-ovario.jpg)
